MMPIP hydrochloride
CAS No. 1215566-78-1
MMPIP hydrochloride( MMPIP hydrochloride (479077-02-6 Free base) )
Catalog No. M27664 CAS No. 1215566-78-1
MMPIP hydrochloride is a selective antagonist of allosteric mGluR7. MMPIP hydrochloride can be used in research on the roles of mGluR7 on central nervous system functions.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 71 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 115 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 192 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 394 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 584 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 833 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameMMPIP hydrochloride
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionMMPIP hydrochloride is a selective antagonist of allosteric mGluR7. MMPIP hydrochloride can be used in research on the roles of mGluR7 on central nervous system functions.
-
DescriptionMMPIP hydrochloride is a selective antagonist of allosteric mGluR7. MMPIP hydrochloride can be used in research on the roles of mGluR7 on central nervous system functions. (In Vitro):In CHO cells coexpressing rat mGluR7 with Gα15, MMPIP hydrochloride inhibits L-(+)-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid (L-AP4; 0.5 mM)-induced intracellular Ca2+ mobilization with an IC50 of 26 nM. MMPIP hydrochloride also antagonizes L-AP4-induced inhibition of cAMP accumulation with an IC50 of 610 nM. MMPIP hydrochloride inhibits L-AP4-induced inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation in CHO cells expressing rat mGluR7.(In Vivo):MMPIP hydrochloride alleviates pain and normalizes affective and cognitive behavior in neuropathic mice. MMPIP hydrochloride (10 mg/kg; i.p.) rescues the MK-801 (0.1 mg/kg)-induced cognitive impairments, by improving the choice accuracy. MMPIP hydrochloride (10 mg/kg) attenuates the amplitude of the acoustic startle response and markedly enhances the prepulse-induced inhibition of the acoustic startle response (up to 137% of control).
-
In VitroMMPIP inhibits L-(+)-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid (L-AP4; 0.5 mM)-induced intracellular Ca2+mobilization in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells coexpressing rat mGluR7 with Gα15 (IC50=26 nM) . In CHO cells expressing rat mGluR7, MMPIP inhibits L-AP4-induced inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation (IC50 220 nM).MMPIP also antagonizes L-AP4-induced inhibition of cAMP accumulation with an IC50 of 610 nM in CHO-human mGluR7/Gα15.
-
In VivoMMPIP (10 mg/kg) attenuates the amplitude of the acoustic startle response and markedly enhances the prepulse-induced inhibition of the acoustic startle response (up to 137% of control).MMPIP (10 mg/kg) rescues the MK-801 (0.1 mg/kg)-induced cognitive impairments, by improving the choice accuracy.Zamifenacin exhibits short elimination half-lives (plasma 1.16 h, brain 1.75 h) following i.p. administration (10 mg/kg) in mice.
-
SynonymsMMPIP hydrochloride (479077-02-6 Free base)
-
PathwayNeuroscience
-
TargetGluR
-
Recptorluciferase
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1215566-78-1
-
Formula Weight369.81
-
Molecular FormulaC19H16ClN3O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 10 mg/mL (27.04 mM)
-
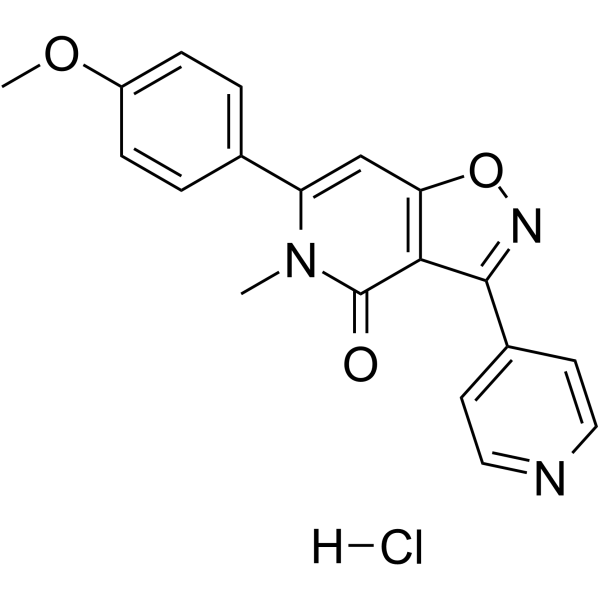
SMILESCl.COc1ccc(cc1)-c1cc2onc(-c3ccncc3)c2c(=O)n1C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Nair AK, Baier LJ. Using Luciferase Reporter Assays to Identify Functional Variants at Disease-Associated Loci. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1706:303-319.
molnova catalog



related products
-
VU 0469650
VU 0469650 is a potent and selective negative allosteric modulator of mGluR1 (IC50 = 99 nM).
-
GET73
GET73 is an negative allosteric modulator of mGluR5. GET73 is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter. GET73 has anti-alcohol and anxiolytic properties.
-
Ziyuglycoside II
Ziyuglycoside II has anticancer, and antitumor properties against gastric cancer and breast cancer cells, by cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


